Prerequisites
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an Extensible Markup Language (XML) standard that allows users to log in to networked but separate websites with just a single login.
To set SAML 2.0 as authentication, make sure you have administrator rights.
After you have logged in as usual in the login mask with your user credentials, click on your name in the upper right corner and then on the settings.
Switch to the Authentication tab in the upper toolbar.
To add a new authentication mechanism, click on the plus icon in the upper right corner.
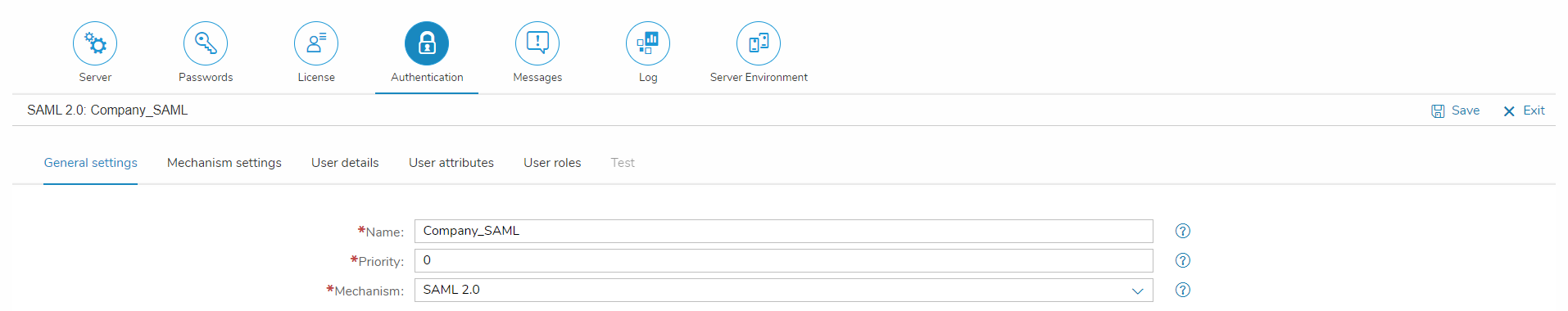
General Settings
| Name | Name under which this authentication mechanism settings is saved |
| Priority | The position of the execution of the respective authentication mechanism – the higher the number, the earlier the respective authentication mechanism is used. If same numbers are available, the sequence is determined lexicographically ascending |
| Mechanism | The authentication mechanism |
Mechanism Settings
| Service Provider Endpoint |
The endpoint URL which needs to be configured in the SAML IDP Provider
|
| Display Name |
The display name is shown on the login button
|
| Force Authentication | If set, the identity provider must authenticate the presenter directly rather than rely on a previous security context. When both ‘Force Authentication’ and ‘Passive’ are activated, the identity provider must not freshly authenticate the presenter unless the constraints of ‘Passive’ can be met |
| Passive | If set, the identity provider and the user agent itself must not visibly take control of the user interface from the requester and interact with the presenter in a noticeable manner |
| Sign Assertions |
If set, also the assertions within the SAML Response will be signed
|
| Validate Issue Instant | When enabled, the issueInstant is validated. In case it is older than a couple of minutes, the authentication is aborted. When enabling this feature, make sure the server time of the IDP and the Simplifier server do not diverge. |
| Sign Out from IDP on logout | When this option is enabled, signing out of Simplifier will also sign the user out of the connected Identity Provider. Only binding type Redirect is supported for logout. Note that this only applies to the user signing out explicitly, not when the token expires. |
| Service Provider Entity ID | By default, the entity ID of your application (the Service Provider) is equal to the callback URL, but you can force your own entity ID by setting this parameter |
| IDP Metadata | XML containing the configuration of your IDP (Identity Provider). Contains e.g. the certificate to sign the communication. This file is usually distributed by your IDP |
| Icon |
Configures an icon, which will be shown on the login page for this authentication mechanism
|